Embrace the Future: The Shift to Pellet Extrusion 3D Printer
Introduction
3D printing is taking leaps and bounds, growing its presence across various industries. Currently, the majority of 3D printing technology relies on Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), which uses thermoplastic filament. But a groundbreaking shift to pellet extrusion 3D printer is underway. This shift is not merely a trend but a significant transformation mirroring the usual availability of polymer products as pellets. Let’s explore why this transition could redefine the future of 3D printing.
From Filament to Pellet Extrusion: A Necessary Transition
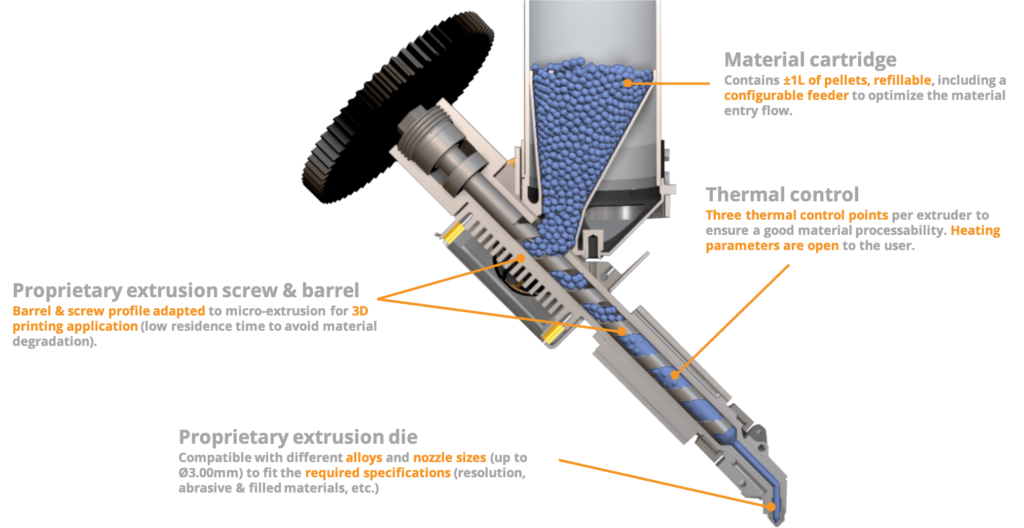
The change from filament to pellets is driven by various convincing reasons. Unlike traditional systems, pellet extrusion eradicates the extra step of manufacturing filaments from plastic pellets. By utilizing plastic pellets directly, the production process is streamlined, leading to faster and more efficient outcomes. The use of filament seems like a passing phase, with pellets likely taking its place in the future.
The Advantages of Pellet Extrusion 3D Printer
Cost-Effective
Pellets are widely used in various industries, which makes them more readily available and affordable. Depending on the volume of purchase, the cost saving can be as much as 65% to 90% compared to filament. This widespread use and lower price make large-scale 3D printing projects more financially accessible.
Variety of Materials
The extensive use of pellets in other businesses has led to a diverse range of types being sold. This variety allows 3D printing to explore new materials and combinations, increasing the possibilities for innovation.
Increased Speed and Greater Print Sizes
Pellet extrusion 3D printers can achieve higher throughput, crafting items more quickly than their filament-based counterparts. This remarkable speed efficiency is key for big and time-sensitive projects and makes larger print sizes more feasible.
Environmental Benefits
Since recycling usually involves breaking down materials into smaller pieces similar to pellets, this form of 3D printing material aligns well with recycling processes. It encourages the reuse of plastics and contributes to more sustainable and eco-friendly practices.

Challenges of Pellet Extrusion 3D Printer
Despite the numerous benefits, there are also drawbacks to consider:
Limited Detail and Geometry
The high speed of pellet extrusion can affect the ability to produce fine details. This is something primarily observed in certain styles of 3D printing, such as robotic-art.
Potential for Print Defects
Inconsistent material intake and output might cause issues such as voids, air bubbles, warping, or improper extruding. The quality of the pellet extruder and original pellet quality can influence these outcomes.
Availability of Pellets
While industrial quantities are easily accessible, small volumes for consumers might be harder to find.
Conclusion
The shift to pellet extrusion in 3D printing marks a significant change in the industry. While there are certain challenges to overcome, the advantages, including cost savings, faster print speeds, and environmental benefits, are promising. Moreover, the ongoing innovations and adaptations in 3D printing technology indicate that these hurdles are surmountable, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future.
Personal Opinion
The transition to pellet-based 3D printing may not be a welcome change for established giants in the filament industry. Their strong foothold could become challenging to maintain as the industry shifts towards pellets—an area already populated by numerous existing players. For newcomers to the 3D printing industry, this transition presents opportunities. This shift is emblematic of an industry in flux, where adaptation and innovation become not just advantageous but essential.